Treatments
WHAT IS IT?
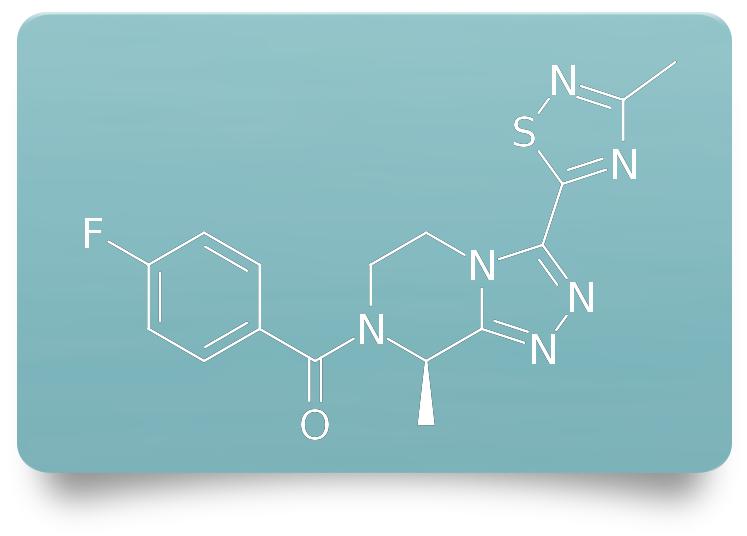
Fezolinetant is a new non-hormonal oral medication taken once per day that is used to treat moderate to severe hot flashes and night sweats. This medicine is called a neurokinin 3 (NK3) receptor antagonist or an NKB antagonist. The medicine blocks the activity of specific neurons in the brain that trigger hot flashes and night sweats in response to declining and variable estrogen concentrations during the menopause transition.
Fezolinetant was approved by the US Food and Drug Administration in May 2023. The cost for a 1-month prescription is over $500 if purchased from a pharmacy without health insurance coverage. Health insurance plans may or may not include coverage for this medication and out-of-pocket costs may change over time.
OUR BOTTOM LINE: DOES IT HELP?
YES. When taken every day, fezolinetant has been shown to reduce hot flash frequency by about 2.5 hot flashes per day, on average, compared to women taking a placebo (an inactive pill). It also reduced hot flash severity ratings, on average, by a small amount. The treatment effects appear similar to postmenopausal hormone therapy and slightly larger than for other nonhormonal treatment options. No studies have directly compared fezolinetant to other medications.

HOT FLASHES AND NIGHT SWEATS

SLEEP DISTURBANCE
MENOPAUSE RELATED QUALITY OF LIFE
POTENTIAL RISKS & SIDE EFFECTS
Side effects are rare but may include the following observed above placebo (background) in 1-2% of people in the studies: abdominal pain diarrhea insomnia back pain, and increases in liver enzymes measured in your blood. Fezolinetant should not be taken by women who have liver cirrhosis or poor kidney function. Certain medications interact with fezolinetant and women taking CYP1A2 inhibitors (some examples include cimetidine, fluvoxamine, ciprofloxacin, amiodarone, interferon) should not take fezolinetant. Clinical trial data from over 2000 people showed liver test elevations were observed in 2.3% of those taking fezolinetant, compared to 0.9% of those taking placebo (1.5% above background risk). Your doctor should monitor your liver function while taking fezolinetant at 3, 6 and 9 months after starting the medication and also if you develop signs of liver injury such as nausea, stomach pain, vomiting, dark urine, flushing, sweating, light colored stools or yellowing of the skin, or eyes.
No long term data is available to assure long term safety. All studies have been 12 weeks to 12 months in duration.
QUALITY OF LIFE EXPECTATIONS
Women taking fezolinetant in the clinical trials experienced small improvements in quality of life similar to hormone therapy and other non-hormonal medications.
REFERENCES
Beaudoin FL, McQueen RB, Wright A, Yeung K, Moradi A, Herron-Smith S, Gutierrez E, Rind DM, Pearson SD, Lin GA. Fezolinetant for Moderate to Severe Vasomotor Symptoms Associated with Menopause: Effectiveness and Value; Evidence Report. Institute for Clinical and Economic Review, December 1, 2022. https://icer.org/assessment/vasomotor-symptoms-menopause-2022/#overview